Can Plant And Animal Cells Perform Cellular Respiration
Respiration is a chain of chemical reactions that enables all living entities to synthesize energy required to sustain.
It is a biochemical process wherein air moves betwixt the external environment and the tissues and cells of the species. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. Every bit an entity acquires energy through oxidising nutrients and hence liberating wastes, it is referred to every bit a metabolic process.
Also refer: Respiration – A Life Process
Let u.s.a. have a look at the respiration in plants notes provided hither to know about the process of respiration, and the different types of respiration that occur in plants.
Do Plants Exhale?
Yes, like animals and humans, plants besides breathe.
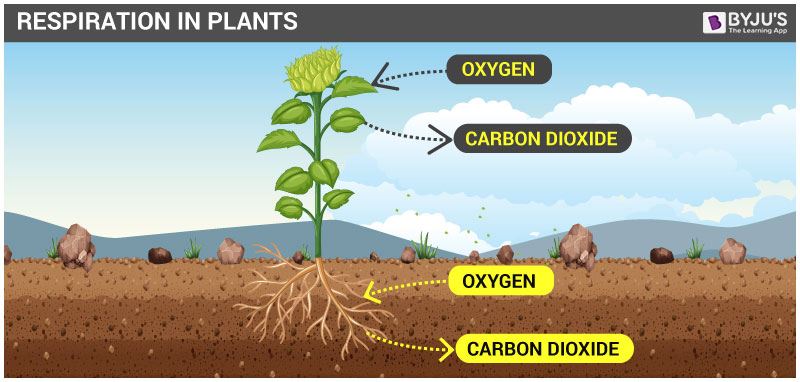
Plants practice require oxygen to respire, the process in return gives out carbon dioxide. Unlike humans and animals, plants practise not possess any specialized structures for exchange of gases, however, they do possess stomata (found in leaves) and lenticels (found in stems) actively involved in the gaseous exchange. Leaves, stems and plant roots respire at a low pace compared to humans and animals.
Breathing is different from respiration. Both animals and humans breathe, which is a step involved in respiration. Plants have role in respiration all through their life as the establish prison cell needs the energy to survive, all the same, plants breathe differently, through a process known equally Cellular respiration.
In this procedure of cellular respiration, plants generate glucose molecules through photosynthesis past capturing energy from sunlight and converting information technology into glucose. Several live experiments demonstrate the breathing of plants. All plants respire to provide energy for their cells to be active or alive.
Let us take a await at the respiratory procedure in plants.
The Process of Respiration in Plants
During respiration, in different plant parts, significantly less substitution of gas takes place. Hence, each function nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements.
Consequently, leaves, stems and roots of plants separately substitution gases. Leaves possess stomata – tiny pores, for gaseous commutation. The oxygen consumed via stomata is used up by cells in the leaves to disintegrate glucose into water and carbon dioxide.
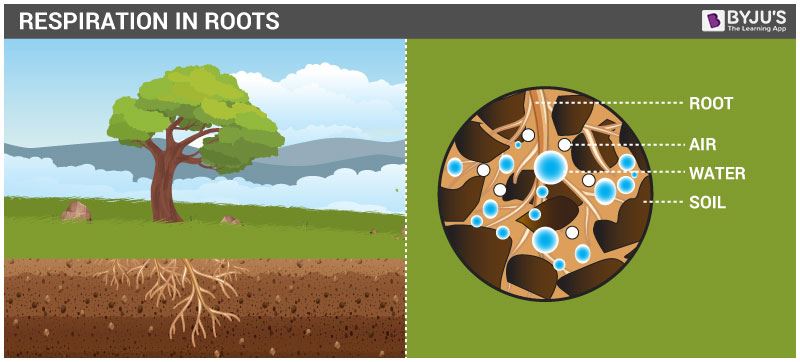
Respiration In Roots
Roots, the underground part of the plants, absorbs air from the air gaps/spaces found between the soil particles. Hence, absorbed oxygen through roots is utilized to liberate the energy that in the hereafter, is used to transport salts and minerals from the soil.
We know that plants possess a specific ability to synthesize their ain food through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis takes place in but those parts of the plants which take chlorophyll, the light-green plant parts. Photosynthesis is and so evident that at times it seems to mask the respiratory process in plants. Respiration must not exist mistaken for photosynthesis. Respiration occurs all through the day, only the photosynthesis procedure occurs in the daytime, in the presence of sunlight only. Consequently, respiration becomes evident at nighttime time in plants.
This is the reason we often hear people warn against sleeping under a tree during nighttime, as it may lead to suffocation due to excess amounts of carbon dioxide liberated by copse post-obit respiration.
Respiration In Stems

The air in case of stem diffuses into the stomata and moves through different parts of the cell to respire. During this stage, the carbon dioxide liberated is also diffused through the stomata. Lenticels are known to perform gaseous exchange in woody or college plants.
Respiration In Leaves
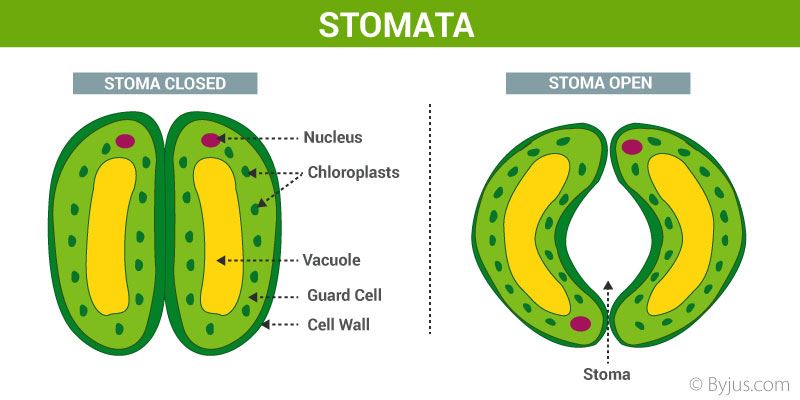
Leaves consist of tiny pores known equally stomata. Gaseous exchange occurs through diffusion via stomata. Guard cells regulate each of the stomata. Substitution of gases occurs with the closing and opening of the stoma between the inferior of leaves and the temper.
Differences between Respiration and Photosynthesis
| Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| This process is common to all light-green plants containing chlorophyll pigments. | This procedure is common to all living things, including plants, animals, birds, etc. |
| Food is synthesized. | Food is oxidised. |
| Energy is stored. | Free energy is released. |
| Is an anabolic process. | Is a catabolic process. |
| Cytochrome is required. | Cytochrome is required here too |
| It is an Endothermal process. | It is an Exothermal procedure. |
| It comprises products such as water, oxygen and sugar | It comprises products such every bit carbon dioxide and hydrogen |
| Radiant energy is converted into potential energy. | Potential free energy is converted into kinetic free energy. |
| Occurs during daytime in the presence of sunlight only. | Is a continuous process, taking place all through the lifetime |
Also, refer to the Departure Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Types of Respiration
There are two main types of respiration.
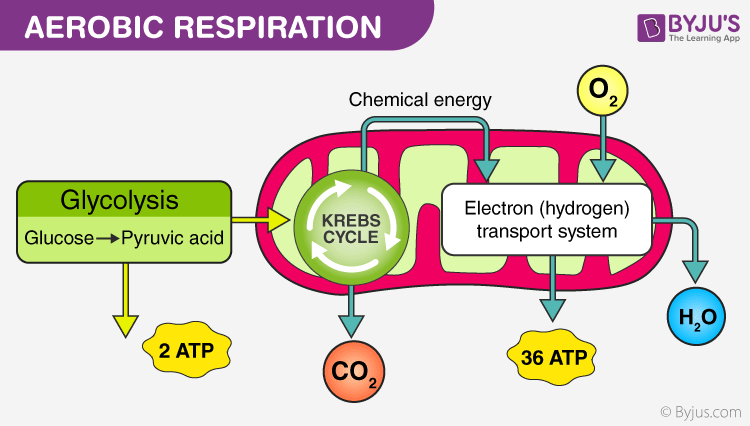
Aerobic Respiration
This type of respiration takes place in the mitochondria of all eukaryotic entities. Food molecules are completely oxidised into the carbon dioxide, water, and energy is released in the presence of oxygen. This type of respiration is observed in all the higher organisms and necessitates atmospheric oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
This type of respiration occurs inside the cytoplasm of prokaryotic entities such as yeast and bacteria. Here, lesser free energy is liberated every bit a event of incomplete oxidation of nutrient in the absence of oxygen. Ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide are produced during anaerobic respiration.
Also, refer to Respiration and its Types
Stay tuned with BYJU'S to learn more nigh Respiration in Plants and other related topics at BYJU'Southward Biological science.
Recommended Video:
Important Questions for you
- How practise plants breathe?
All light-green plants exhale through the procedure of Cellular respiration. In this process, nutrients obtained from the soil are converted into energy and are used for dissimilar cellular activities.
- Practise plants breathe at nighttime?
Yes, plants breathe throughout its life span both during the twenty-four hour period and night. The chemical equation of cellular respiration is expressed as — oxygen + glucose -> carbon dioxide + water + oestrus energy.
- Proper noun the respiratory organ in woody stems.
In hard and woody stems, respiration or the exchange of gases takes place through lenticels. They are the small pores, scattered all over the bark and are plant in all trees.
- What is the office of stomata in plant's respiration?
Stomata are the tiny pores located on the epidermis of leaves, stems and other organs. During cellular respiration, stomata facilitate gaseous exchange by opening and endmost of the pores.
- Which role of roots is involved in the exchange of respiratory gases?
Root hairs, the tubular extensions of the epidermis are involved in the exchange of respiratory gases.
Register at BYJU'S for more on respiration in plants notes for reference.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/plant-respiration/
Posted by: partainovertutremew.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Can Plant And Animal Cells Perform Cellular Respiration"
Post a Comment